THE 12 HUE COLOR WHEEL
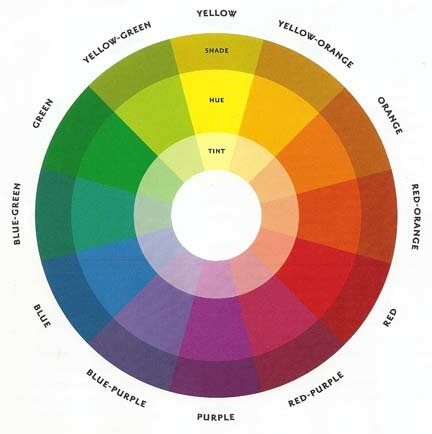
Color Value

Color Value
Each hue is
at a level of full saturation, or
brightness. There is no black or white added. When the relative amount of white
or black is added to a hue, the color
has lightness and darkness, called value.
To show value, the color wheel has more rings: two outer for dark shades and two inner for light tints.
Color
Schemes
No color
stands alone. A color is always seen in the context of other colors. In fact,
the effect of a color is determined by the light reflected from it, the colors
that surround it; or the perspective of the person looking at it. No one color
is “good” or “bad”. Rather, it’s one part of a composition that as a whole is pleasing or not.
Types of Color Schemes

Types of Color Schemes
Monochromatic: This palette has
the dark, medium and light values of a single
color. It has no color depth, but it provides the contrast of dark, medium and
light that’s important to good design.

Analogous: These are adjacent colors. They share strong undertones which create pleasing, low-contrast harmony. Analogous palettes are rich and always easy to work with.



Complement: These are colors directly opposite of each other on the color wheel. Complementary colors are contrasting, convey energy, vigor and excitement.

Split Complement: These are colors one step either way of the complement’s own analogous colors. It’s strength is in the low-contrast beauty of analogous colors, plus the added accent of an opposite color.
The 4-Step Color Palette Process:
Color not
only adds impact and dimension, it contributes significantly to image
legibility, organization, and mood.
Here is a 4-step process to find rich and engaging colors for your design:
Step 1: Clearly define the results you want to achieve with color.
Step 2: Select a main, key color that reflects the needs of the project.
Step 3: Select a color scheme based on the key color (hue).
Step 4: Experiment and refine the scheme’s color choices in terms of the project requirements.
*some sections adapted from pagethinker.com
Here is a 4-step process to find rich and engaging colors for your design:
Step 1: Clearly define the results you want to achieve with color.
Step 2: Select a main, key color that reflects the needs of the project.
Step 3: Select a color scheme based on the key color (hue).
Step 4: Experiment and refine the scheme’s color choices in terms of the project requirements.
*some sections adapted from pagethinker.com

No comments:
Post a Comment